McKinsey menyatakan bahwa Indonesia pada tahun 2030 menjadi 7 negara terkuat. Goldman Sachs memprediksi ekonomi Indonesia akan terus menguat hingga mencapai posisi 4 besar dunia pada tahun 2045. Ramalan terbukti... Read more
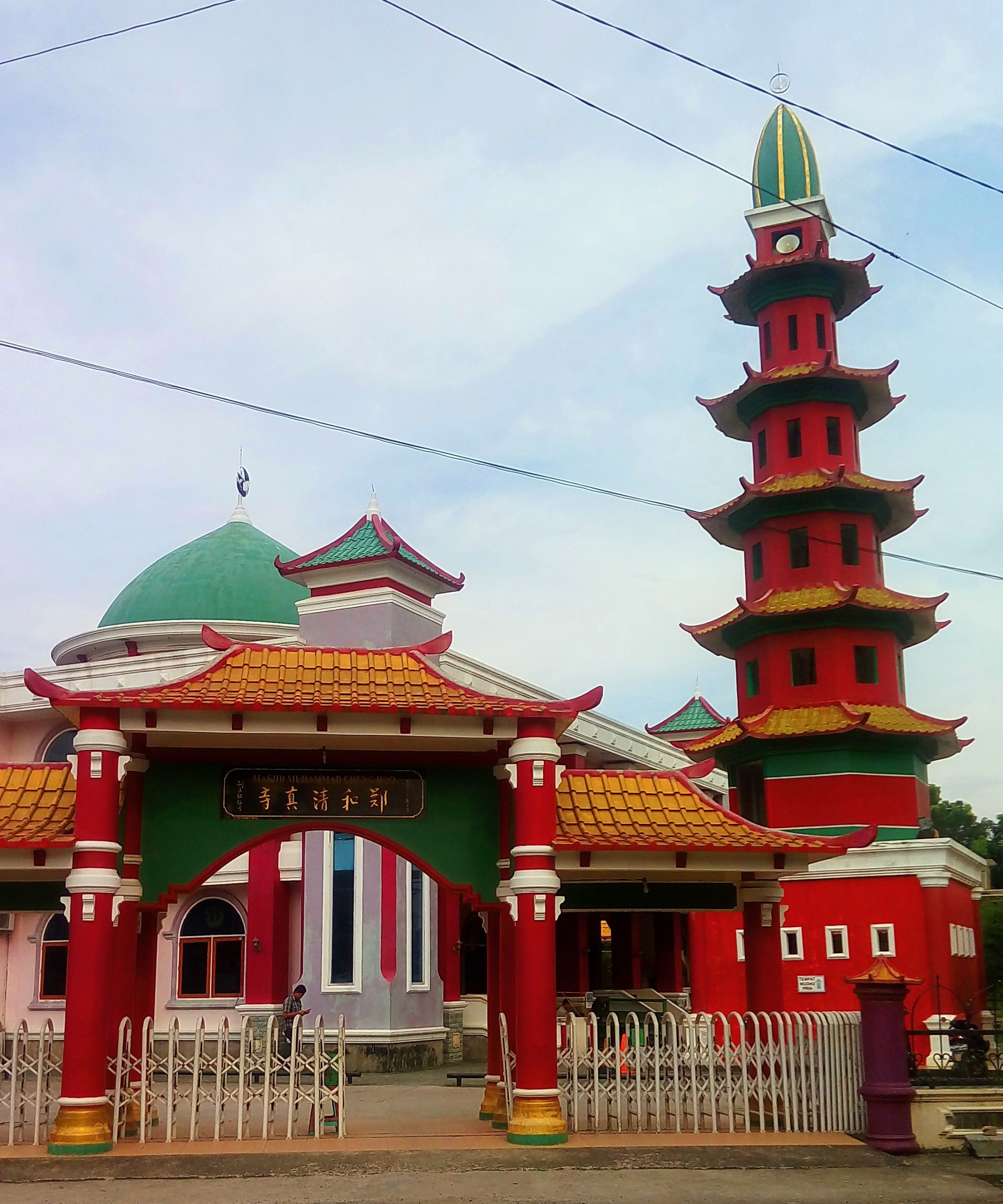

Beberapa catatan tentang Cheng Ho dalam penyiaran Islam di Nusantara sebagai berikut: a. Majalah National Geographic menyatakan Cheng Ho adalah seorang Tionghoa muslim, berdasar data eksplorasi, bukan sekadar legenda. b.... Read more

UTS Teori Ekonomi Makro klas A1 Sebutkan ruang lingkup pembelajaran teori ekonomi makro Sebutkan dan jelaskan bagian-bagian yang terdapat pada arus siklus kegiatan ekonomi makro. Jika arus kegiatan ekonomi terganggu,... Read more

1.Suka duka perjalanan karir. 2.Manfaat networking dalam karir. 3.Membangun personal branding untuk menjalin relasi. 4.Tips dan trik untuk memperluas networking bagi mahasiswa. Silahkan klik file berikut jika ingin mengetahui lebih... Read more

•Pandemi menuntut kita menyesuaikan cara baru. •Tabligh terbuka tidak boleh diadakan dengan alasan protokol kesehatan. •Metode online sebagai alternatif dalam berdakwah. •Umat Islam sangat membutuhkan sugesti dan kekuatan rohani secara... Read more








